Environment
Society
Human capital
- Human Rights
- Development of Human Resource
- Development of Global Human Resource
- Diverse Human Resource and Diverse Working Styles
- Health Management to Enhance Corporate Value
- Occupational Safety and Health
- Occupational Safety and Health
- Business Continuity
- Business Continuity Plan/Management (BCP/BCM)
- Communication
- Procurement Activities
- Stakeholder Engagement
- Social Contribution Activities
Governance
Technological Strengths
Fujikura Group annually checks the progress of each item set out in its Sustainability Goals 2025. These goals are linked to Fujikura Group Long-Term Environmental Vision 2050, and priority measures include targets for reducing GHG (greenhouse gas) emissions and responding to the TCFD (Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures). By checking progress annually and considering future measures, we have established a system that enables appropriate responses.
Identifying and responding to climate change risks and opportunities
We are identifying potential risks and opportunities in the transition to a low-carbon economy.
In order to analyze how climate change will affect business growth of Fujikura Group, we take into account long-term predictions from international research organizations (OECD, IPCC) and other sources, as well as societal concerns and customer requests for responses to climate change.
Identified risks are reviewed appropriately.
risk
| Classification | Climate change risks | Future Actions | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2°C scenario (Transition risk) Short term/medium term |
Policy and legal risks |
|
|
| Technology Risk |
|
||
| Market Risk |
|
||
| Reputation risk |
Requests for disclosure of information and responses to climate change from customer, investors, and various rating agencies |
||
| 4°C scenario (physical risk) Medium term/long term |
Acute risks |
|
|
| Chronic Risk |
|
||
opportunity
| Each business | Social Trends | opportunity |
|---|---|---|
| Telecommunication Systems |
|
|
| Electronics |
|
|
| Automotive Products |
CASE Progression
|
|
| Power Systems |
|
|
| Real Estate |
Promoting the use of digital technology
|
|
Responding to risks
Responses to identified risks and future considerations are approval and decided by the Global Environment committee, chaired by the the chairperson of the committee in charge of the Environment. Along with reporting on the results of action plans established in the CSR priority measures, the Global Environment committee shares information, considers and approval response plans, and reports to the Sustainability strategy Meeting. In addition, environmental data such as electricity usage, water, and disposal from each Fujikura Group site is entered, evaluated, and analyzed, and the Global Environment committee confirms results and reviews plans twice a year.
Investing in opportunities
Demand Fiber Optic Cable, Fujikura Group's main product, is expected to increase due to the increase in global information and communication traffic. In addition, due to the growing demand for reducing greenhouse gas emissions triggered by global warming, it is expected that customer will demand products with lower greenhouse gas emissions during manufacturing. Seeing this as an important opportunity for Fujikura Group, we have constructed and started operation of a new SWR™ factory at our Sakura business. This new factory has installed rooftop solar panels, making it carbon neutral.

Financial impact
Fujikura Group has made the following investments to date in preparation for future disaster risks.
Fujikura Sakura business has experienced a slope collapse accident caused by heavy rain in the past. In recent years, the frequency of heavy rain has increased due to climate change, so the plant has been working on slope improvement from 2016 to 2019 (cost: 580 million yen).
Nishi Nippon Electric Wire's Oita Factory faces Oita Bay and is at risk of damage from storm surges and tsunamis during typhoons. In response to this, in fiscal 2017 we constructed a new office building where 500 employees can take refuge (cost: 460 million yen).


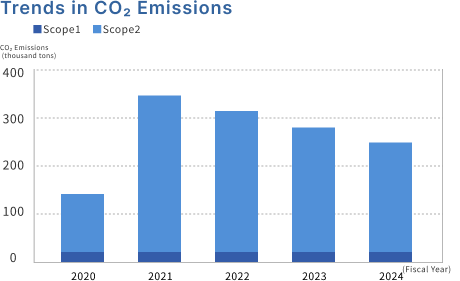
CO2 Emissions Reduction policy and guideline
Fujikura Group has established its Environmental Management Action guideline for 2025. As a RE100 target, the Group has set a CO2 reduction target of "achieving a renewable energy rate of 45% by fiscal 2030," and has set this as a common target for its overseas bases as well.
To reduce total CO2 emissions, we will obtain SBT certification in July 2023, with targets of reducing Scope 1 and 2 emissions by 33% by fiscal year 2030 (compared to fiscal year 2020), and reducing Scope 3 emissions by 15% by fiscal year 2030 (compared to fiscal year 2020).
Calculation method for CO2 emissions
- Fujikura Group 's CO2 emissions are calculated by multiplying the amount of energy consumed by each type of energy each fiscal year by the CO2 emission coefficient for each type of energy.
- Compliant with the market-based method outlined in the GHG Protocol's Scope 2 guidance
- Base year Domestic and overseas: Fiscal year 2020
- Emission Factor
Domestic electricity: Adjusted emission factors by electricity business for the most recent fiscal year published by the Ministry of the Environment and the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry
Overseas electricity: Residual mix emission factor for the most recent fiscal year by country and grid. If no applicable factor exists, average emission factor.
Domestic and overseas fuels: Emission coefficients for the most recent fiscal year published by the Ministry of the Environment
Total GHG emissions
Total 236,000 tons
Domestic emissions: 105,000 tons
Overseas emissions: 131,000 tons
Amount of CO₂ offsets through non-fossil fuel certificates both domestically and internationally
Domestic: FIT non-fossil certificate 14,000 tons
Overseas: (Kingdom of Thailand) I-REC 35,000 tons (China) Green Power Certificate 9,000 tons
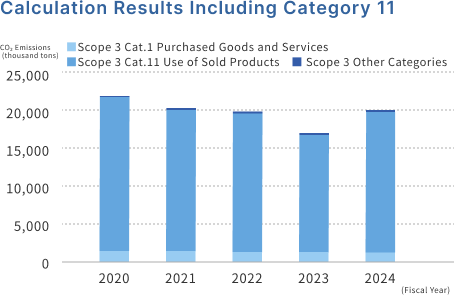
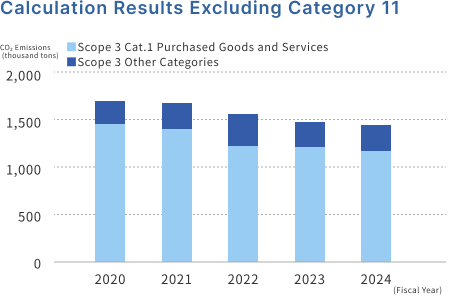
Supply chain emissions (Scope 3)
Upon obtaining SBT certification in July 2023, Fujikura expanded the scope of Scope 3 calculations and disclosure from the domestic group to the overseas group*1. We have reviewed our category classifications and are now calculating emissions from downstream categories that we had not been able to calculate before. "Category 11: Use of sales products*2" is the largest, but this is emissions due to transmission losses in the electric wires and cables sales by Fujikura Group companies.
Fujikura Group 's Scope 3 emissions
*1 The calculation scope for Fujikura Group was determined by application the GHG Protocol's control criteria to organization boundaries, so emissions from the AFL Group are not included in the calculation.
*2 Emissions from Category 11 transmission losses are calculated from power losses due to Joule heat generation. Estimates were used for the calculations because it was difficult to obtain data on cable usage rates. To make it easier to see the transition of Fujikura's Scope 1, 2 and main category emissions, we have created graphs that include and exclude Category 11.
FY2024 Activity Results
As part of Fujikura Group 2025 Environmental Management Activity guideline (25 Environmental guideline), we worked towards the goal of "reducing CO₂ emissions by 13.2% or more compared to fiscal 2020" in fiscal 2024. We are continuing to implement energy-saving activities across the entire company, contributing to reducing emissions. For measures that result in particularly large reductions, we are promoting information sharing and application at other bases to maximize the reduction effect. CO₂ emissions (market standard) for the entire Fujikura Group, including offsets through non-fossil fuel certificates, were 236,000 tons, a 31% decrease compared to fiscal 2020.
Major Initiatives for Fiscal Year 2024
-
1. Reduction of CO₂ emissions from Fujikura
- Energy conservation: Develop innovative Monodukuri to improve productivity and business competitiveness, and actively promote conventional energy conservation activities
- Energy creation: Decision made to introduce renewable energy using solar power generation (3 locations)
Start of operations: 2 (Sakura business SWR™ new factory, new real estate business building)
Currently in use: 3 (Sakura business parking lot, Fujikura Electronic Components (Thailand) Ltd., Fujikura Conec (THAILAND) LTD.) - Energy Procurement: Procurement of appropriate environmental certificates and renewable energy that meet the requirements of RE100, etc.
-
2Reducing CO2 emissions in the supply chain
- Promoting resource reuse
- Conducted a survey of major raw material manufacturers regarding carbon dioxide emissions reduction
Transportation and mobility activities
Regarding the improvement of energy intensity associated with Butsuryu activities, we had targeted a 4% improvement in fiscal 2024 from the actual figure of 41.2 KL/kiloton in fiscal 2020, but due to the transfer of a high-proportion group companies, we set the target at 61.5 KL/kiloton, the same as the previous year, excluding the impact.In contrast, the actual figure for fiscal 2024 was 60.9 KL/kiloton, achieving the target with a 1% improvement.
We also continue to promote the efficient use of resources, and are promoting the reuse of packaging materials and wooden drums.Furthermore, we are actively promoting the use of a two-tier stacking jig (official name: electric wire drum pallet), which was developed to improve loading efficiency.
Reuse of packaging materials and wooden drums


Energy saving initiatives
Promotion of Cool Biz and Warm Biz
As an environmentally friendly corporate group, Fujikura Group promotes Cool Biz in the summer and Warm Biz in the winter, striving to achieve both seasonal comfort and energy conservation.
Updated air conditioners, updated lighting to LED
In fiscal 2024, we will continue to work on updating air conditioners and converting lighting to LED.
Air conditioner renewal is being actively promoted in Thailand, where energy consumption is high.
The conversion to LED lighting has begun at multiple locations, but we are particularly moving ahead with the conversion to LED lighting at our Sakura business.
Initiatives at group companies
Many bases are seeing an increase in production volume in fiscal 2024. As a result, domestic and overseas group companies are further promoting holiday mode (a mode that reduces power consumption of equipment on holidays), narrowing air-conditioned areas with partitions, creating equipment downtime by adjusting production, shortening idle time, changing operating conditions, and other measures to actively eliminate wasteful energy use.
Water Risk Management policy and guideline
To address water risks, Fujikura Group has set "minimizing water usage in factories and managing wastewater" as a challenge item in its Long-Term Environmental Vision 2050. Regarding minimizing water usage in factories, we are working under the slogan "Don't use it, use it repeatedly, clean it and return it to nature." Regarding wastewater management, we recommend that domestic manufacturing sites install constant monitoring systems for "pH," "oil content," and "turbidity" in the final wastewater basin.
In addition, in Fujikura Group 2025 Environmental Management Action guideline, which are based on the Long-Term Environmental Vision 2050, we have set a target of improving water usage per unit of production by 5% or more in fiscal 2025 compared to fiscal 2020 at consolidated company in Japan and overseas, and are working toward this goal.
Understanding water risk areas and their relationship to Fujikura Group 's business development
The United Nations Water Conference, held in March 2023, discussed "urgently scaling up activities to ensure equitable access to water for all." The resulting "Water Action Agenda" included over 700 commitments to promote the transformation from a water-critical world to a water-secure world. In its 2021 report*, the United Nations Water committee (UN-Water) noted significant changes in surface water levels in one-fifth of the world's river basins over the past five years, highlighting climate change-related impacts such as the drying of lakes in arid regions and the expansion of lakes due to melting glaciers and permafrost. Furthermore, in its 2021 report**, the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) identified northern China, South Asia, and the Mediterranean coastal region as hotspots of water stress. Fujikura Group, which business in China, Southeast Asia, Europe, North America, and South America, continues to recognize the need to address water risks.
At each domestic base, we check hazard maps and take into account past disaster situations to assess the risk of water disasters such as floods, inland water, and tsunamis, as well as the risk of drought, and then consider and implement countermeasures.Specifically, bases with relatively high risks are prepared for water disasters, with the Fujikura Butsuryu West Japan Distribution Center equipped with emergency drainage pumps and the Nishi Nippon Electric Wire & Cable Oita business and Hasama business equipped with waterstops.
Additionally, at our overseas manufacturing sites, we conduct actual risk assessments for river flooding, coastal flooding, and drought after checking Aqueduct. Fujikura Electronics Vietnam Ltd. (FEVL) and Fujikura Conec (THAILAND) LTD. (FCTL), which have been determined to be at high risk of flooding, have established emergency measures and clarified policy for water stoppage and evacuation to prepare for disasters.
* Progress on Freshwater Ecosystems 2021:
https://www.unwater.org/sites/default/files/app/uploads/2021/09/SDG6_Indicator_Report_661_Progress-on-Water-related-Ecosystems_2021_EN.pdf
**2021 STATE OF CLIMATE SERVICES
https://library.wmo.int/doc_num.php?explnum_id=10826
***Water stress: The amount of water resources required for agriculture, industry, energy, and the environment is said to be 1,700 m3 per person per year. When the amount of available water falls below 1,700 m3, it is considered to be in a state of "water stress," when it falls below 1,000 m3, it is considered to be in a state of "water shortage," and when it falls below 500 m3, it is considered to be in a state of "absolute water shortage."
Past water risks that occurred at Group sites
In 2011, Fujikura Group's manufacturing bases in the Kingdom of Kingdom of Thailand suffered major damage (water damage) from a flood that occurred in Kingdom of Thailand, said to be a once-in-50-year event. Although the company declared recovery from the flood in 2016, the experience has led to the decentralization of manufacturing bases to neighboring countries and the installation of waterproof walls. Since then, the company has been working on flood and drought as part of its BCP activities in Thailand. In addition, the selection of new bases is decided after thorough research into past floods and altitude.
Initiatives for fiscal 2024
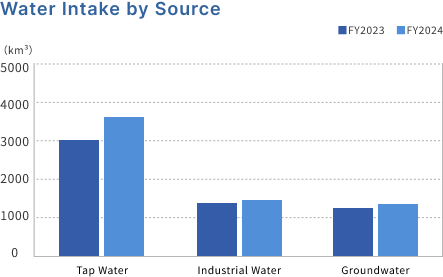
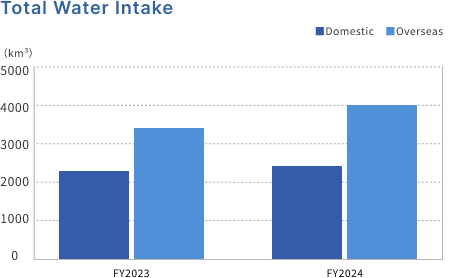
Total water withdrawals in Japan and overseas, and water withdrawals and usage by water resource
Fujikura Group aims to ensure that the amount of water withdrawn and used in its business activities is equal.
Regarding water intake, there is no water stress caused by drought in Japan, but preventative measures against flooding are being implemented, such as improving slopes, strengthening stormwater gutters, and reinforcing seawalls.
Due to expanded production, total water usage in fiscal 2024 will increase from fiscal 2023 both domestically and overseas. By water source, there will be an increase in tap water, and slight increases in industrial water and well water.
Domestic wastewater volume
Domestic wastewater volume in fiscal 2024 is expected to increase by 6.2% compared to fiscal 2023. The volume of wastewater also increased due to increased well water usage at restarted factories. Almost all domestic bases automatically monitor the pH, turbidity, and oil content of wastewater at the final drainage basin.

