Technology Areas/Product Groups
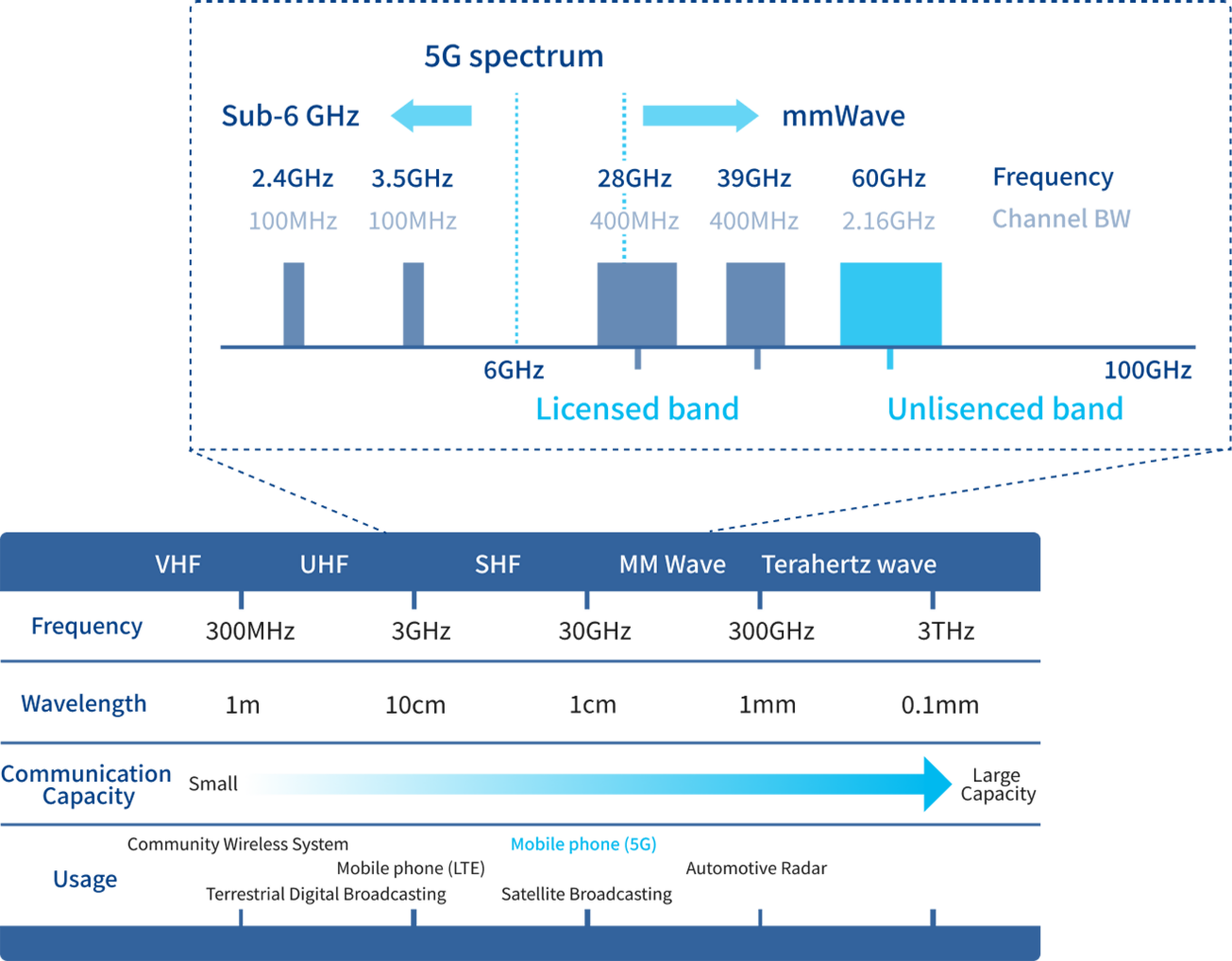
Millimeter waves use frequencies more than 10 times those of conventional microwave bands, providing a much wider bandwidth than microwaves. This broadband makes it possible to realize high-speed, large-capacity communications, high-resolution radar, sensors, and more. However, compared to microwaves, millimeter waves have the disadvantage of being more easily blocked by obstacles and therefore less likely to reach long distances. They also have the advantage of being highly confidential and less prone to unwanted interference.
The fifth-generation mobile communications system (5G), a typical application of millimeter waves, uses a high-gain antenna (phased array antenna) that concentrates radio waves into a sharp beam and radiates them strongly in a specific direction to ensure long-distance transmission. This reduces energy radiation in unnecessary directions, and because of its wide bandwidth, it requires one-tenth the energy to transmit the same amount of data as microwaves. Due to these effects, it has been reported that 5G millimeter wave wireless communications reduces CO2 emissions per unit of data by approximately 85%.
For more details, please see the special website below and LinkedIn.

