Technology Areas/Product Groups
Optical Fiber
To realize the information and communications infrastructure that supports the evolution of IoT (Internet of Things), it is essential to establish an optical communications network that exceeds the existing transmission capacity limits. Optical fibers will play a central role in this. NTT's IOWN concept has set three target performance targets: low power consumption, high capacity and high quality, and low latency, and is considering the introduction of various new technologies.
As part of Fujikura's efforts to realize the IOWN concept, we have released the world's highest density optic fiber cable, which incorporates our proprietary 12-fiber intermittently bonded ribbon fibers, "Spider Web Ribbon®. " We are further evolving this technology and developing an ultra-high-density optic fiber cable incorporating optical fibers with a 200 µm outer diameter that is thinner than the standard coating.
Furthermore, as part of our research and development to achieve even higher densities, we are developing multi-core fibers, in which multiple cores are arranged in a single optical fiber cladding. With an eye toward the early practical application of multi-core fibers, we are focusing on multi-core fibers with four cores arranged in a single optical fiber cladding, which has the same diameter (125 µm) as the standard optical fiber currently in use and is optically compatible with existing single-mode fibers.


Optical Connector
Optical connectors precisely align Optical Fiber and bring their end faces into close proximity or contact, achieving low-loss, highly reliable, repeatable connections. They are application in single-fiber and multi-fiber connectors (Figure 1), each with multiple connection methods. Fujikura possesses core technologies in each connection method and offers a variety of solutions tailored to customer applications. PC connection physically connects the end faces Optical Fiber. Fujikura has been developing low-loss and multi-fiber optical connectors using high-precision polishing and precision resin molding technologies. In addition to PC connection, we also offer field-assembled optical connector solutions (Figure 2) that combine refractive index matching materials and Fusion Splicer. In recent years, the increasing data traffic volume in hyperscale data center (HSDCs) has led to increased demand for high-density optical connectors and optical wiring solutions. To address this challenge, Fujikura is expanding into this new field with its compact, high-density MMC ferrule connectors (Figure 3), a key component, and wiring solutions. In addition, we are developing products compatible with 80 µm clad Optical Fiber, which will enable even greater miniaturization and density. To achieve even greater density, we are also working on developing a multi-core optical connector, the MCF-MPO connector (Figure 4), which assembles multi-core fibers with multiple cores in a single fiber.
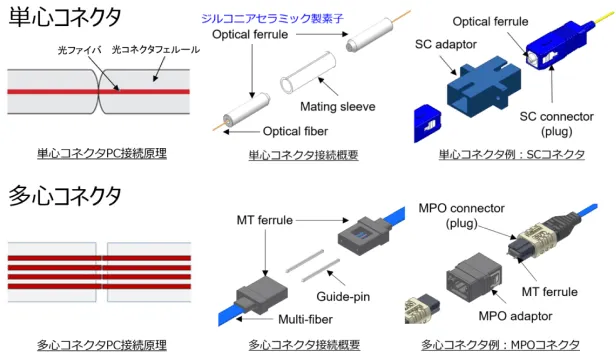
Figure 1: Single-fiber connector and multi-fiber bulk connector

Figure 2: Examples of field-assembled connectors (Left: fusion-type MPO connector, Right: refractive index-matched single-fiber connector)
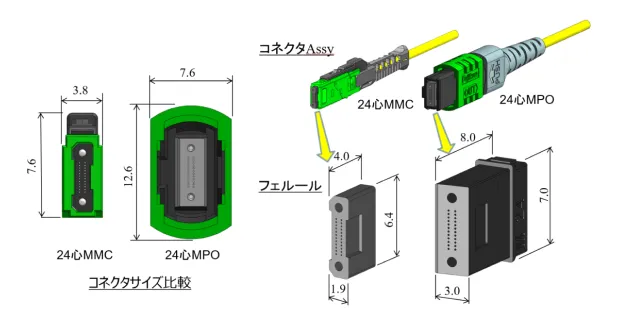
Figure 3: MMC vs MPO connector comparison

Figure 4: Multicore fiber (left) and MCF-MPO connector (right)
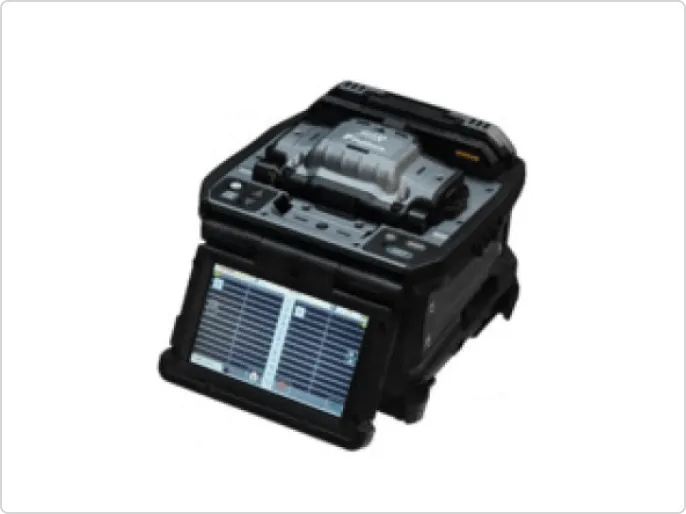
Fusion Splicer
Fujikura is currently researching and developing an optical fiber fusion splicer. These devices measure the positon of the core of an optical fiber with high precision and align two optical fibers at the submicron level using a precision axis alignment mechanism. Fusion splicing is then performed using either quasi-corona discharge or CO2 lasers. Quasi-corona discharge fusion splicers using tungsten electrodes are compact and are primarily used to connect optical fibers for communication. On the other hand, CO2 laser-based fusion splicers are primarily used to process specialty optical fibers because tungsten does not adhere to the optical fibers. The properties of CO2 lasers are utilized not only for splicing, but also for processing tip lenses and fabricating optical couplers. This device utilizes mechatronics technology and has established a leading position in the global market.



High-density Fiber Optic Cable
- ①Increased the number of laying in existing conduits while still using the existing laying method
- ②Shortened splicing time by using SWR® to splice ribbons together
- ③Reduced connection points by laying in a single line from outdoors to inside the premises
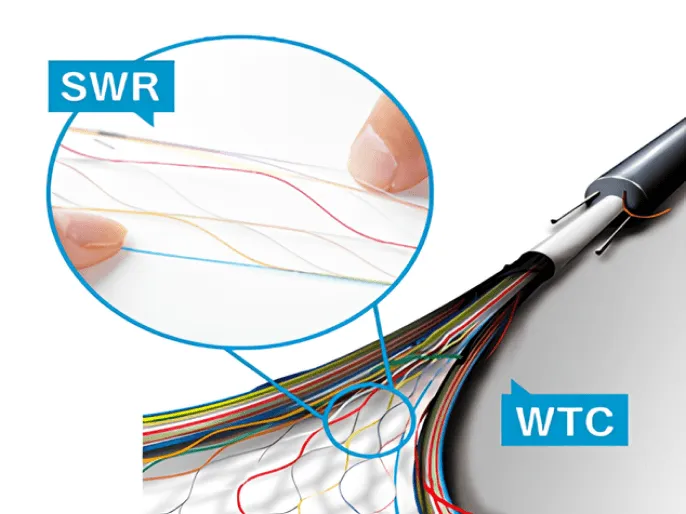
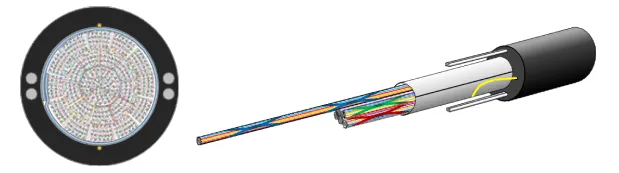
Ultra-thin high-density WTC®
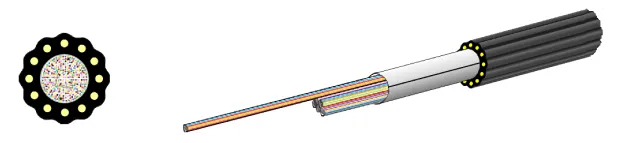
Air-blown WTC® (AB-WTC™)
Ultra-fine coaxials
Micro Coaxial Cable Assembly
In recent years, micro coaxial cables have been used in a variety of applications, including mobile devices, wearable devices, and drones, creating a need for connections with high bending and twisting characteristics in extremely limited spaces, as well as smaller diameters, noise resistance, and high-speed signal transmission.
Therefore, we are developing micro coaxial cables and assemblies for internal wiring of equipment that meet these needs by improving the internal structure of the cables.
The photo below is an example of a highly flexible micro-coaxial cable. By changing the material and configuration of the central conductor, we have achieved bending performance that is more than 10 times greater than that of conventional cables. This cable can be designed and manufacturing to meet the required bending performance.
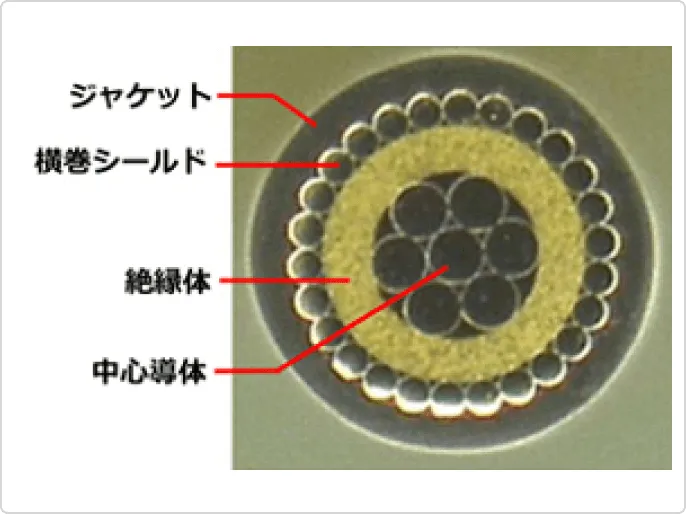
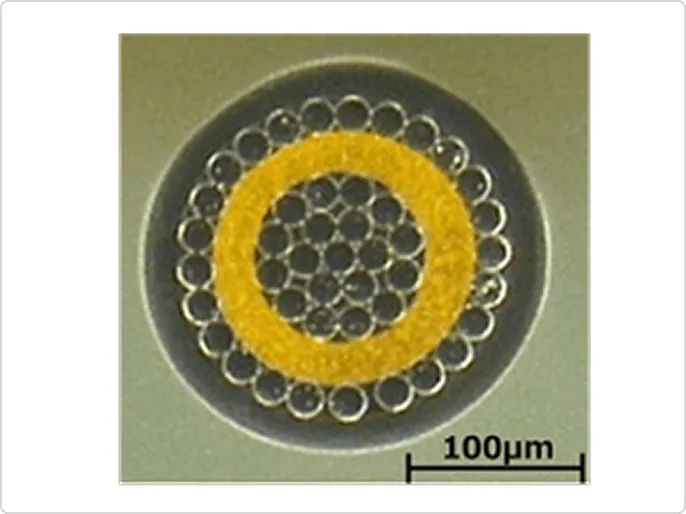
Sensors
Pressure Sensors
As the name suggests, pressure sensors are sensors used to measure gas pressure. They are used in a wide range of fields, including industrial equipment such as pressure switches, medical equipment such as blood pressure monitors, and consumer products.
Currently, Fujikura is leveraging its development technology for high-precision pressure sensors that combine piezo-resistive pressure sensors with signal processing ICs to achieve high output stability and improved accuracy.
The pressure range is from 2 kPa in the micro-pressure region to 1 MPa in the high-pressure region, and the output is compatible with analog output and digital output (I2C™, SPI), and various package shapes are available.
In 2024, we released a 4x4 mm compact pressure sensor (AT7) to contribute to the miniaturization and thinning of electronic devices.
We will continue to strengthen our product lineup to meet the increasingly diverse needs of the market.
Oxygen Sensors
Oxygen sensors are used to measure oxygen concentration and are used in a wide range of fields, including medical equipment such as oxygen concentrators and incubators, and industrial equipment such as nitrogen generators.
The oxygen sensor is a limiting current type that uses a zirconia solid electrolyte that has oxygen ion conductivity at high temperatures. Fujikura will manufacturing high-precision oxygen sensors by utilizing its ceramic molding technology, packaging technology, assembly technology, and measurement technology.



Millimeter Wave
The introduction of the fifth-generation mobile communications system (5G) is progressing in order to provide high-quality video streaming and various applications utilizing VR/AR. 5G will further increase the speed and capacity of mobile networks, enabling highly reliable, ultra-low latency communications and multiple simultaneous connections. These aspect will not only improve the convenience of everyday life, but also serve as infrastructure that will create new added value, such as increasing the efficiency of industry and society.
As a technology that realizes high-speed, large-capacity, and low-latency communications, 5G has newly introduced millimeter waves (radio waves of approximately 30 GHz or higher). Millimeter waves have an extremely wide bandwidth and can achieve breakthrough high-speed communications. However, compared to conventional microwaves (below a few GHz), they are more likely to be attenuated and deteriorated due to various factors, so the materials, design, and manufacturing of various devices used in communication equipment require completely different ideas and advanced technologies. Fujikura is conducting research and development to improve the performance and cost of millimeter-wave band communication devices. In the 60 GHz band, we have developed a 60 GHz millimeter-wave wireless communication module that integrates a phased array antenna and a signal processing unit, achieving world-class communication speed (more than 1 Gbps) and long-distance transmission (more than 500 m) at the same time (This is an example of the performance value in the experimental environment, depending on the surrounding environment). In addition, we have developed a 28 GHz mmWave antenna board of the FutureAccess™ Type-C series that integrates peripheral functions including high-frequency ICs (RF-ICs) and RF-ICs, phased array antennas, and power supply circuits in the 28 GHz band, aiming to application 5G base stations. In addition, we are developing low-loss, high-performance devices in the mmWave band, such as bandpass filters, to comprehensively support the new generation of mmWave communication devices.

60 GHz millimeter wave wireless communication module

28 GHz mmWave Antenna Board

