Technology Areas/Product Groups
Planar wiring parts
FPC
FPC is promoting product and technology development that focuses on deepening its presence in the mobile and electronic device fields, which have traditionally been its main market, and responding to the growing new needs of the automotive market.
Mobile and Electronic Devices
As electronic information devices evolve, we are promoting development to support ever higher density and resolution. In addition, with the increase in data transmission volume due to 5G and other technologies, we are also working on development to support high frequency and high speed transmission.
<High-definition technology>
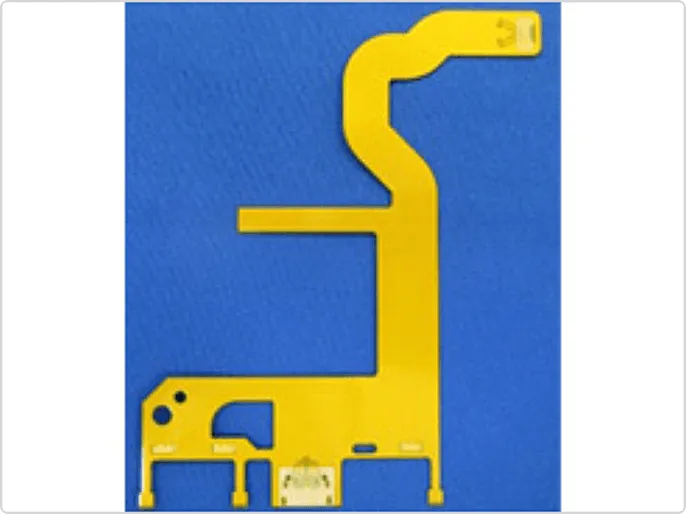
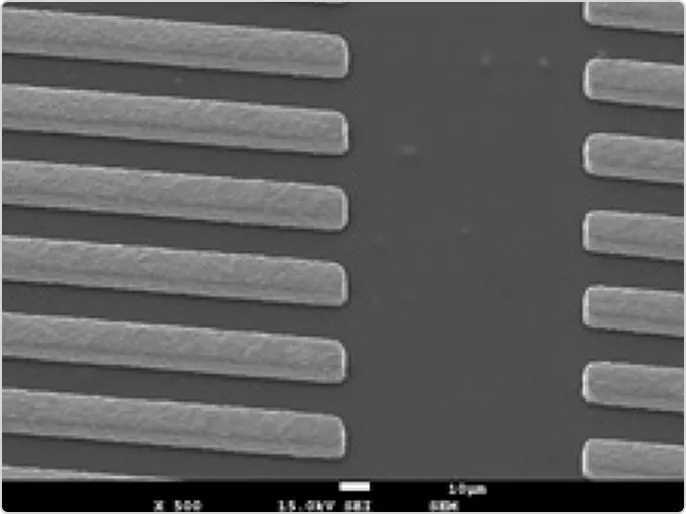
We are currently developing high-definition circuit formation technology using the semi-additive method, aiming for practical mass production of L/S=10/10 µm (see Photo 1).
<High frequency, high speed transmission FPC>
We are currently developing an FPC for internal wiring of devices that uses low dielectric constant and low dielectric loss tangent materials compatible with 5G, as well as an antenna substrate for the millimeter wave band (28 GHz) (see Photo 2).

In-vehicle
As automobiles become more electronic, application of FPCs in in-vehicle applications is expanding, and we are promoting development to meet the needs for new functions and performance.
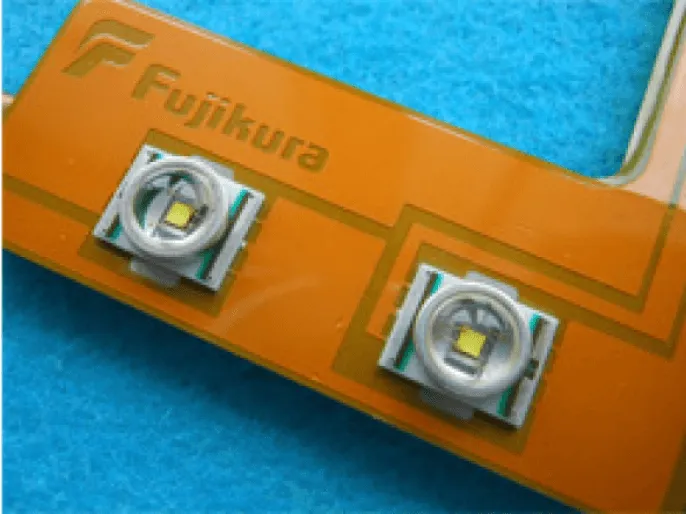
<High heat dissipation FPC>
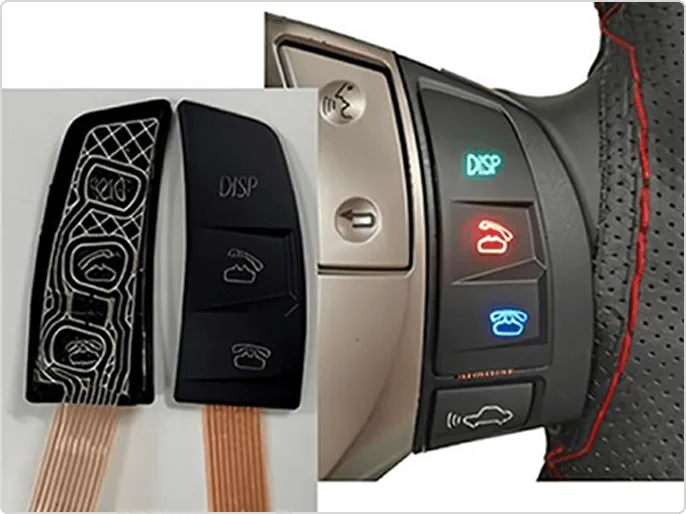
For automotive LED lighting, headlamps have high output, and the heat generated by the LEDs must be efficiently dissipated. We have developed an FPC with high heat dissipation properties by using materials with excellent heat dissipation properties and a product structure (see Photo 3).
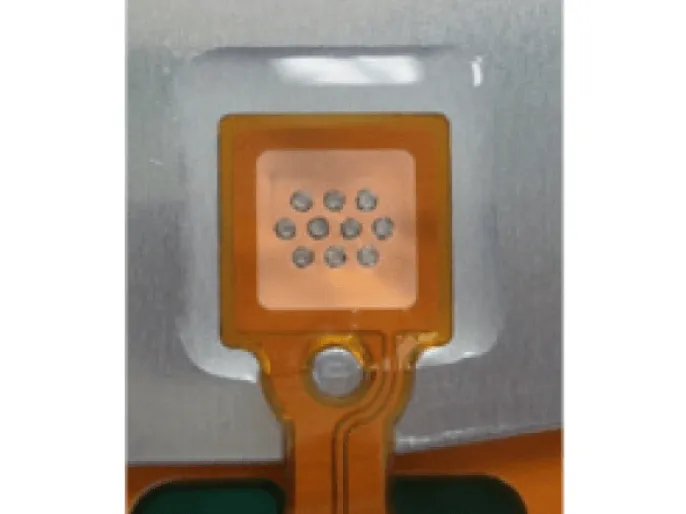
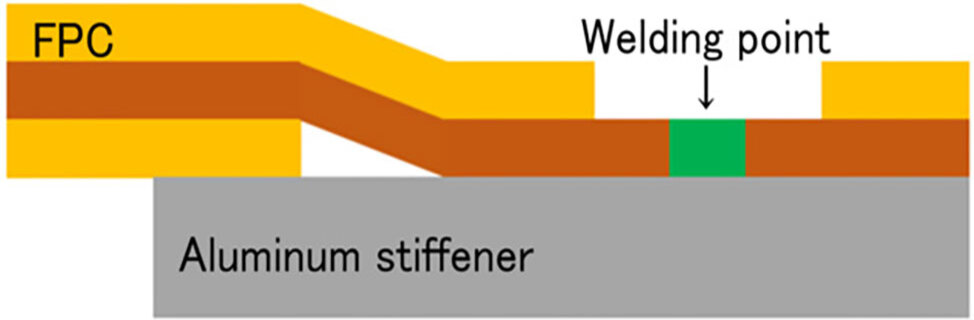
<Dissimilar metal joining technology>
There is a demand for the development of FPCs that use aluminum reinforcing plates as current paths for application in high-current applications. Fujikura's unique welding method using a fiber laser was application to the copper and aluminum welding required for this, achieving a joint that suppresses the formation of intermetallic compounds (see Photo 4 and Figure 1).


Solid wiring parts
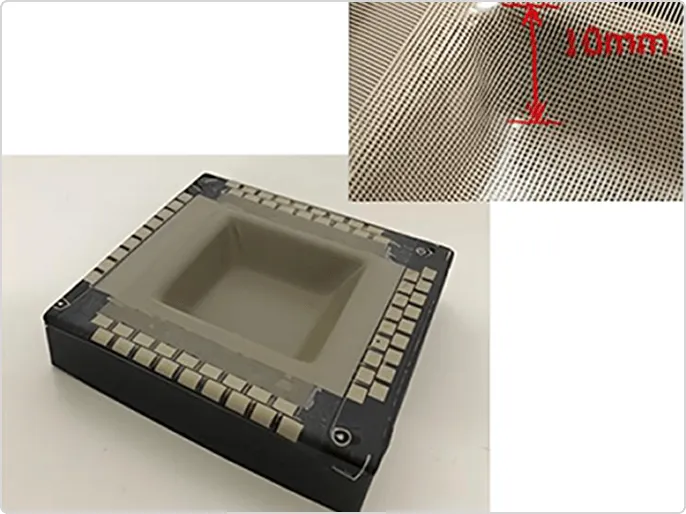
Fujikura has developed a three-dimensional wiring component that integrates electronic circuits with a plastic housing. This technology makes it possible to form three-dimensional shapes without destroying flat printed circuits, and to form electronic circuits on plastic parts with uneven or curved surfaces.
This technology makes it possible to form multilayer circuits on molded parts made of ABS or polycarbonate with a molding angle of 90° and irregularities of up to 10 mm.
This technology, which simultaneously creates three-dimensional circuits and processes resin for molding, significantly improves the traditional assembly process of manually creating three-dimensional flexible circuit boards. Furthermore, it is expected to improve product design and reduce the number of parts, making it suitable for use in home appliances and automotive products.


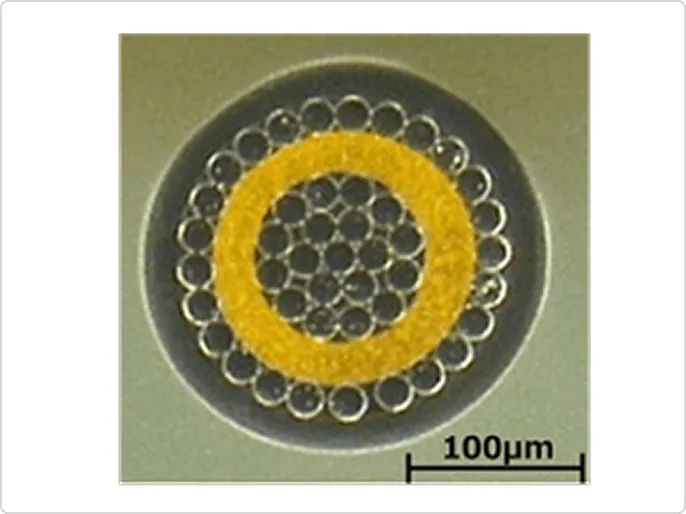
Ultra-fine coaxials
Micro Coaxial Cable Assembly
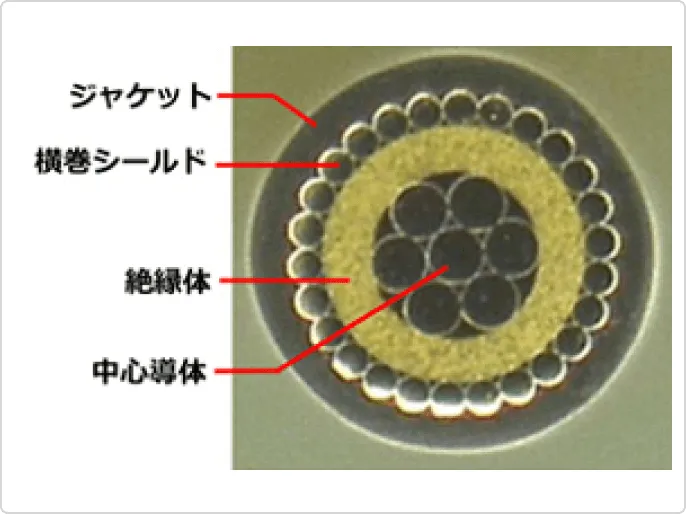
In recent years, micro coaxial cables have been used in a variety of applications, including mobile devices, wearable devices, and drones, creating a need for connections with high bending and twisting characteristics in extremely limited spaces, as well as smaller diameters, noise resistance, and high-speed signal transmission.
Therefore, we are developing micro coaxial cables and assemblies for internal wiring of equipment that meet these needs by improving the internal structure of the cables.
The photo below is an example of a highly flexible micro-coaxial cable. By changing the material and configuration of the central conductor, we have achieved bending performance that is more than 10 times greater than that of conventional cables. This cable can be designed and manufacturing to meet the required bending performance.
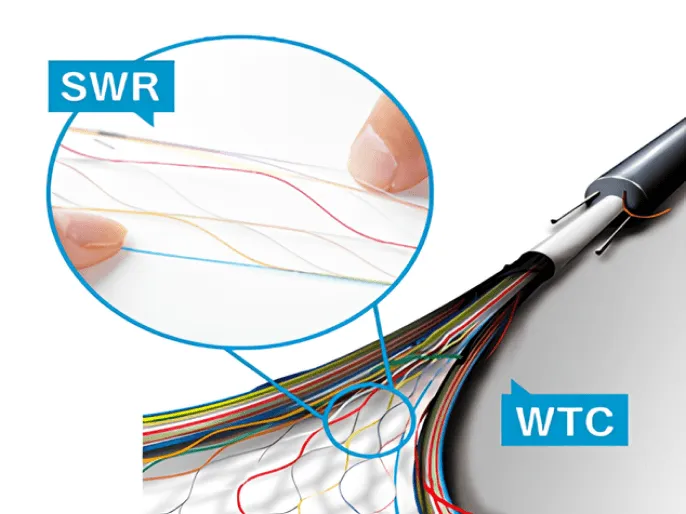
High-density Fiber Optic Cable
- ①Increased the number of laying in existing conduits while still using the existing laying method
- ②Shortened splicing time by using SWR® to splice ribbons together
- ③Reduced connection points by laying in a single line from outdoors to inside the premises
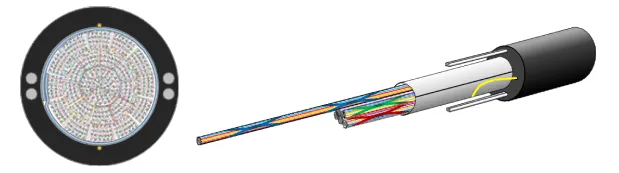
Ultra-thin high-density WTC®
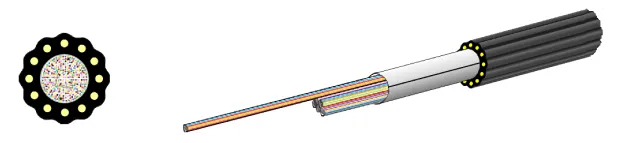
Air-blown WTC® (AB-WTC™)
Electric Connectors
For over 60 years, Fujikura has been developing, manufacturing, quality control (QC) and sales original connectors.
In recent years, there has been an increasing demand for smaller and lighter mobile devices, including smartphones, and connectors are also being required to be "ultra-low profile," "ultra-compact," and "highly easy to mate."
To meet these market needs, Fujikura is working to develop connectors that are both compact, lightweight, and multifunctional.
To meet these ever-increasing demands, we will continue to hone the following technologies and develop the world's top-level ultra-miniature connectors.
Design Technology
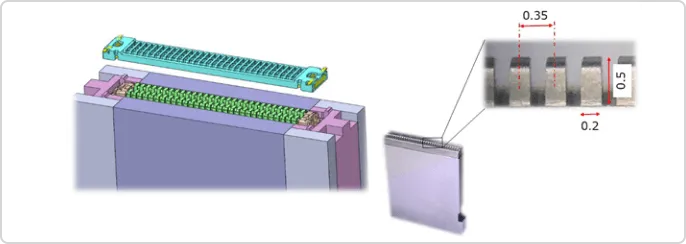
- Structural analysis technology developed over many years to ensure contact reliability
- Flow analysis technology that allows resin to be filled even in thin walls (FTTH)
Production Engineering
- Press die manufacturing technology, press processing technology
- Resin molding die manufacturing technology, thin-walled resin molding technology
- High-speed automatic inspection, assembly, and packaging technology
- Gold-saving plating technology for ultra-small terminals
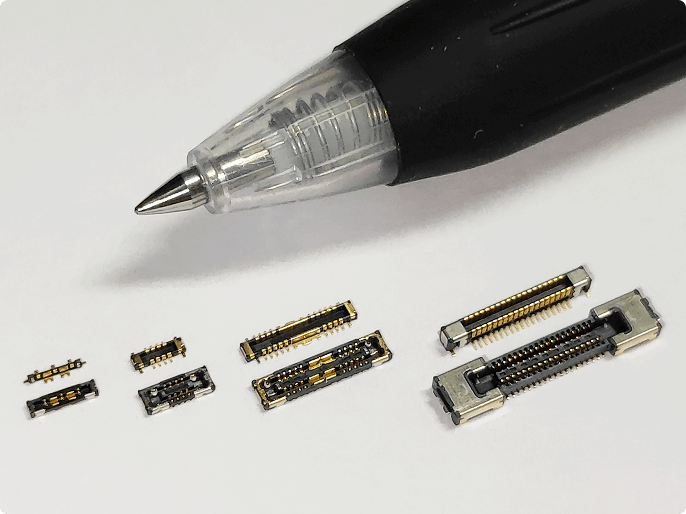
Board-to-board connector (FB3A series)



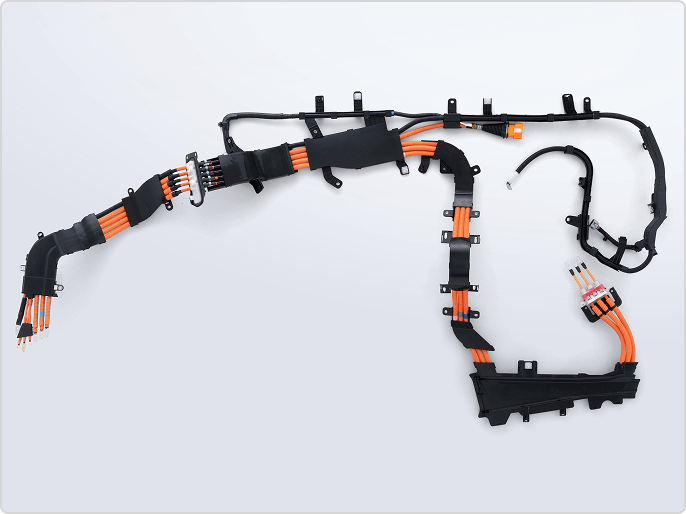
Wire Harness
Wire harness, which are often referred to as the "nerves and blood vessels of a car," are bundles of wires that act as electrical pathways to ensure the proper operation of electronic units inside the car, connecting power and signals to every corner of the car.
With the increasing electronics content of in-vehicle equipment every year, Wire harness are becoming more complex.
Fujikura utilizes the latest technology and the wisdom and experience it has cultivated over many years to comprehensively develop and manufacturing Wire harness, from wiring materials and in-vehicle wiring systems to fuse boxes, connectors, and terminals.
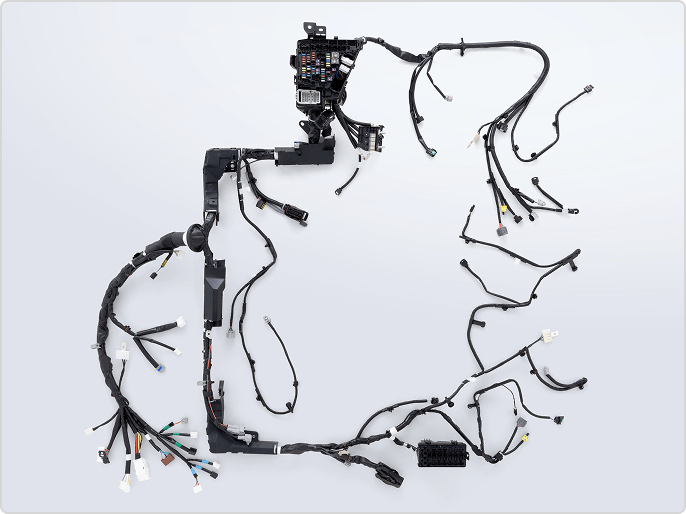
Heat Transport Devices
Power semiconductor cooling module
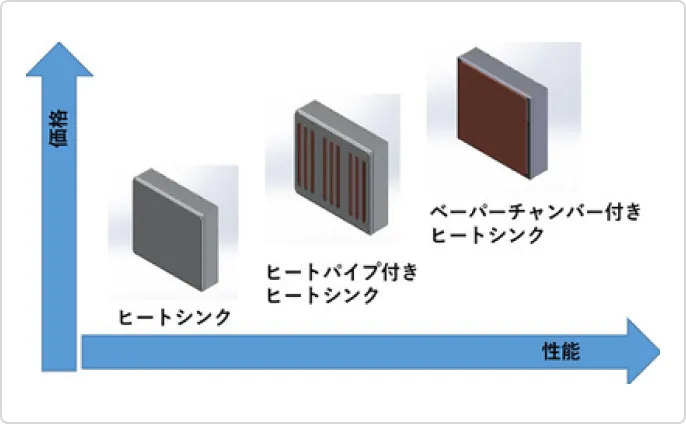
We are developing large-capacity heat pipes and vapor chambers to dissipate heat from power semiconductors that generate large amounts of heat. Vapor chambers are flat heat pipes that have high heat dissipation performance because the entire surface acts as a heat pipe. We are also working on improving the internal structure to increase maximum heat transport capacity and reduce thermal resistance.
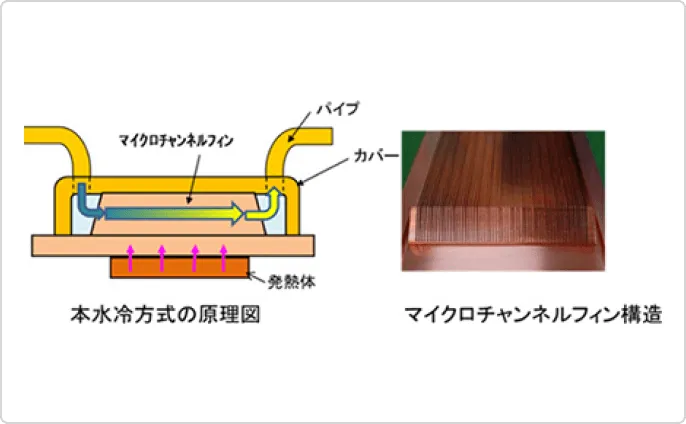
Cold plate for high performance computer
We have developed a liquid cooling unit called a cold plate, which uses a microchannel fin structure (fin thickness: 0.15 to 0.4 mm) to dissipate heat from large computers such as supercomputers and mainframes. This cold plate requires less space than air-cooled systems, yet provides several times more cooling performance.